What are the uses of carbon dating
Contents:
However, when an organism ceases to exist, it no longer takes in carbon from its environment and the unstable 14 C isotope begins to decay. From this science, we are able to approximate the date at which the organism were living on Earth.
What is Radiocarbon Dating?
Radiocarbon dating is used in many fields to learn information about the past conditions of organisms and the environments present on Earth. Radiocarbon dating usually referred to simply as carbon dating is a radiometric dating method. It uses the naturally occurring radioisotope carbon 14C to estimate the age of carbon-bearing materials up to about 58, to 62, years old.
Uses of Radiocarbon Dating Climate science required the invention and mastery of many difficult techniques. These had pitfalls, which could lead to controversy. It is used in Radiocarbon dating of an object. The main purpose of this technique is to make an estimate of the age of that object and the best part is, the estimate.
Carbon has two stable, nonradioactive isotopes: There are also trace amounts of the unstable radioisotope carbon 14 C on Earth. Carbon has a relatively short half-life of 5, years, meaning that the fraction of carbon in a sample is halved over the course of 5, years due to radioactive decay to nitrogen The carbon isotope would vanish from Earth's atmosphere in less than a million years were it not for the constant influx of cosmic rays interacting with molecules of nitrogen N 2 and single nitrogen atoms N in the stratosphere.
How Does Carbon Dating Work
Both processes of formation and decay of carbon are shown in Figure 1. Diagram of the formation of carbon forward , the decay of carbon reverse. Carbon is constantly be generated in the atmosphere and cycled through the carbon and nitrogen cycles. Once an organism is decoupled from these cycles i. When plants fix atmospheric carbon dioxide CO 2 into organic compounds during photosynthesis, the resulting fraction of the isotope 14 C in the plant tissue will match the fraction of the isotope in the atmosphere and biosphere since they are coupled.
Radiocarbon dating
After a plants die, the incorporation of all carbon isotopes, including 14 C, stops and the concentration of 14 C declines due to the radioactive decay of 14 C following. This follows first-order kinetics. The currently accepted value for the half-life of 14 C is 5, years. This means that after 5, years, only half of the initial 14 C will remain; a quarter will remain after 11, years; an eighth after 17, years; and so on.
- ghost matchmaking.
- oc dating sites.
- Radiocarbon Dating - Chemistry LibreTexts.
The equation relating rate constant to half-life for first order kinetics is. In samples of the Dead Sea Scrolls were analyzed by carbon dating. From the measurement performed in the Dead Sea Scrolls were determined to be years old giving them a date of 53 BC, and confirming their authenticity.

Carbon dating has shown that the cloth was made between and AD. Thus, the Turin Shroud was made over a thousand years after the death of Jesus. Describes radioactive half life and how to do some simple calculations using half life. The technique of radiocarbon dating was developed by Willard Libby and his colleagues at the University of Chicago in He was awarded Nobel Prize for this work. In the upper atmosphere, nitrogen 14 7 N is bombarded by cosmic ray to produce 14 6 C: Radioactive carbon 14 6 C gets converted to radioactive carbon dioxide 14 CO 2.
This radioactive 14 CO 2 is taken up by plants during photosynthesis.
The entire process of Radiocarbon dating depends on the decay of carbon The results were summarized in a paper in Science in , in which the authors commented that their results implied it would be possible to date materials containing carbon of organic origin. Tricks also spread through visits between laboratories and at meetings, and sometimes even through publications. He was awarded Nobel Prize for this work. For decades after Libby performed the first radiocarbon dating experiments, the only way to measure the 14 C in a sample was to detect the radioactive decay of individual carbon atoms. From the measurement performed in the Dead Sea Scrolls were determined to be years old giving them a date of 53 BC, and confirming their authenticity.
However, when a plant dies, it can no longer fix up radioactive 14 CO 2. As a result, the concentration of 14 6 C in it starts decreasing. The half-life of a 14 6 C is years.
Thus in 11, years the 14 6 C concentration is reduced to one fourth of its initial concentration. Thus, by measuring the concentration of 14 6 C in a dead carbon-containing object, and knowing the concentration of 14 6 C in a living plant, were can estimate the age of the object the age of the object means the number of years ago when plant should have died , by using the formula.
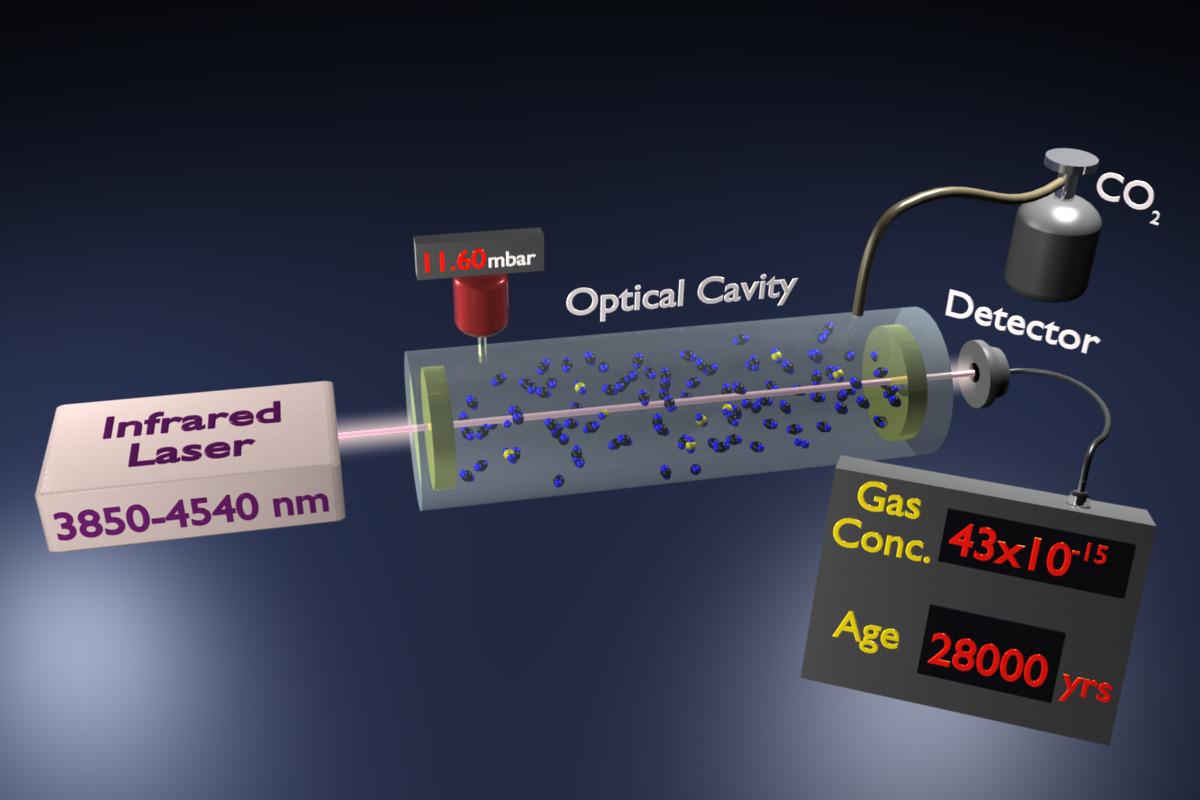
Estimating the age of a carbon-containing object by measuring the concentration or activity of 14 6 C in it, is called radiocarbon dating. The age of glaciers, snow fields, and even wines can be estimated by radioisotopic dating. In these cases, the radioactivity level of tritium an isotope of hydrogen having mass number of 3 3 1 H is measured.