How do we use radiometric dating
Contents:
We have also obtained a very similar age by measuring Pb isotopes in materials from earth. I should mention that the decay constants basically a value that indicates how fast a certain radioactive isotope will decay for some of these isotope systems were calculated by assuming that the age of the earth is 4. The decay constants for most of these systems have been confirmed in other ways, adding strength to our argument for the age of the earth.
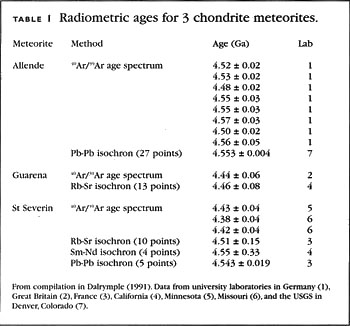
Radiometric dating depends on the chemistry and ratios of different elements. It works like this:. Take, for example, zircon, which is a mineral; its chemical formula is ZiSiO 4 , so there is one zirconium Zi for one silicon Si for four oxygen O. One of the elements that can stand in chemically for zircon is uranium. Uranium eventually decays into lead, and lead does not normally occur in zircon, except as the radioactive decay product of uranium.
Therefore, by measuring the ratio of lead to uranium in a crystal of zircon, you can tell how much uranium there originally was in the crystal, which, combined with knowing the radioactive half-life of uranium, tells you how old the crystal is. Obviously, if the substance you are measuring is contaminated, then all you know is the age since contamination, or worse, you don't know anything, because the contamination might be in the opposite direction - suppose, for example, you're looking at radio carbon carbon 14, which is produced in the atmosphere by cosmic rays, and which decays into nitrogen.
Since you are exposed to the atmosphere and contain carbon, if you get oils from your skin onto an archeological artifact, then attempting to date it using radio carbon will fail because you are measuring the age of the oils on your skin, not the age of the artifact. This is why crystals are good for radiometric dating: The oldest crystals on Earth that were formed on Earth are zircon crystals, and are approximately 4. Asteroids in the solar system have been clocked at 4.
We assume that the Earth is probably as old as the asteroids, because we believe the solar system to have formed from a collapsing nebula, and that the Earth, being geologically active, has simply destroyed any older zircon crystals that would be its true age, but we can't really be certain. The building blocks that the Earth is made of, the asteroids are 4. Based on astronomical models of how stars work, we also believe the Sun to be about 4.
Radiometric dating is a widely accepted technique that measures the rate of decay of naturally occurring elements that have been incorporated into rocks and fossils. Every element is defined by the particular number of protons, neutrons, and electrons that make up it's atoms. Sometimes, the number of neutrons within the atom is off. These atoms, with an odd number of neutrons, are called isotopes. Because they do not have the ideal number of neutrons, the isotopes are unstable and over time they will convert into more stable atoms.
Navigation menu
Scientists can measure the ratio of the parent isotopes compared to the converted isotopes. The rate of isotope decay is very consistent, and is not effected by environmental changes like heat, temperature, and pressure. This makes radiometric dating quite reliable. To learn more, visit our Earning Credit Page.
At a certain temperature, the crystal structure has formed sufficiently to prevent diffusion of isotopes. For a half life of years, the following table shows the fraction remaining for various time periods:. For example, uranium is an isotope of uranium, because it has 3 more neutrons in the nucleus. Not sure what college you want to attend yet? Choose one Student Teacher Parent Tutor. So, what exactly is this thing called a half-life? Learning Outcomes As a result of watching this video, you might be able to:
Not sure what college you want to attend yet? The videos on Study. Students in online learning conditions performed better than those receiving face-to-face instruction.
Explore over 4, video courses. Find a degree that fits your goals. Learn about half-life and how it is used in different dating methods, such as uranium-lead dating and radiocarbon dating, in this video lesson.
Try it risk-free for 30 days. An error occurred trying to load this video. Try refreshing the page, or contact customer support. Register to view this lesson Are you a student or a teacher?
Radiometric dating - Wikipedia
I am a student I am a teacher. What teachers are saying about Study. Conditions of Fossil Preservation: Are you still watching? Your next lesson will play in 10 seconds. Add to Add to Add to. Want to watch this again later? What is Radioactive Dating? Principles of Radiometric Dating. Relative Dating with Fossils: Index Fossils as Indicators of Time. Methods of Geological Dating: Numerical and Relative Dating. What is Relative Dating? Absolute Time in Geology. What is Carbon Dating? Methods for Determining Past Climates. Applications of Nuclear Chemistry.
- dating fat girl site.
- maxie gh dating.
- You must create an account to continue watching!
- UCSB Science Line.
- !
Introduction to Physical Geology: Intro to Natural Sciences. Middle School Earth Science: Weather and Climate Science: UExcel Weather and Climate: Guns, Germs, and Steel Study Guide. Holt McDougal Introduction to Geography: Radiometric dating is used to estimate the age of rocks and other objects based on the fixed decay rate of radioactive isotopes. Radiometric Dating The aging process in human beings is easy to see. Radioactive Decay The methods work because radioactive elements are unstable, and they are always trying to move to a more stable state.
Half-Life So, what exactly is this thing called a half-life? Uranium-Lead Dating There are different methods of radiometric dating that will vary due to the type of material that is being dated. Potassium-Argon and Rubidium-Strontium Dating Uranium is not the only isotope that can be used to date rocks; we do see additional methods of radiometric dating based on the decay of different isotopes. Radiocarbon Dating So, we see there are a number of different methods for dating rocks and other non-living things, but what if our sample is organic in nature?
Try it risk-free No obligation, cancel anytime.
Radiometric dating
Want to learn more? Select a subject to preview related courses: Lesson Summary Let's review. Learning Outcomes As a result of watching this video, you might be able to: Compare radiometric dating, radioactive decay and half-life Understand that uranium-lead dating is one of the most reliable radiometric dating methods Relate the processes of potassium-argon and rubidium-strontium dating Determine how radiocarbon dating works and recognize why it is important.
Unlock Your Education See for yourself why 30 million people use Study. Become a Member Already a member? The mathematical expression that relates radioactive decay to geologic time is [12] [15]. The equation is most conveniently expressed in terms of the measured quantity N t rather than the constant initial value N o.
The above equation makes use of information on the composition of parent and daughter isotopes at the time the material being tested cooled below its closure temperature. This is well-established for most isotopic systems. Plotting an isochron is used to solve the age equation graphically and calculate the age of the sample and the original composition.
Radiometric dating has been carried out since when it was invented by Ernest Rutherford as a method by which one might determine the age of the Earth. In the century since then the techniques have been greatly improved and expanded.
Radiometric dating. Geologists use radiometric dating to estimate how long ago rocks formed, and to infer the ages of fossils contained within those rocks. Radiometric dating or radioactive dating is a technique used to date materials such as rocks or carbon, in which trace radioactive impurities were selectively.
The mass spectrometer was invented in the s and began to be used in radiometric dating in the s. It operates by generating a beam of ionized atoms from the sample under test.
'+(f.options.tagName!==false?f.options.tagName:f.options.Random?a.RandomTitle:a.RecentTitle)+"
The ions then travel through a magnetic field, which diverts them into different sampling sensors, known as " Faraday cups ", depending on their mass and level of ionization. On impact in the cups, the ions set up a very weak current that can be measured to determine the rate of impacts and the relative concentrations of different atoms in the beams.
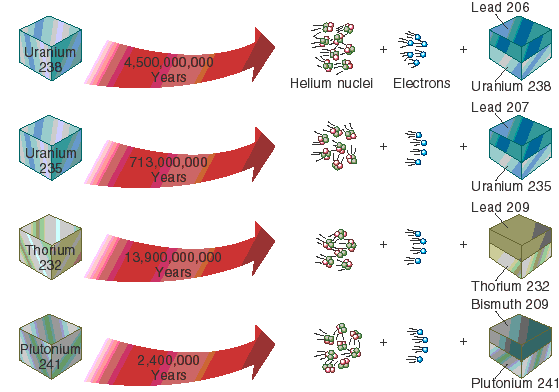
Uranium—lead radiometric dating involves using uranium or uranium to date a substance's absolute age. This scheme has been refined to the point that the error margin in dates of rocks can be as low as less than two million years in two-and-a-half billion years. Uranium—lead dating is often performed on the mineral zircon ZrSiO 4 , though it can be used on other materials, such as baddeleyite , as well as monazite see: Zircon has a very high closure temperature, is resistant to mechanical weathering and is very chemically inert.
- Radiometric Dating: Methods, Uses & the Significance of Half-Life.
- .
- !
- im dating the ice princess wattpad cast.
- speed dating cherbourg 2020.
- unsingle dating app.
- are you dating anyone in spanish.
Zircon also forms multiple crystal layers during metamorphic events, which each may record an isotopic age of the event. One of its great advantages is that any sample provides two clocks, one based on uranium's decay to lead with a half-life of about million years, and one based on uranium's decay to lead with a half-life of about 4.
This can be seen in the concordia diagram, where the samples plot along an errorchron straight line which intersects the concordia curve at the age of the sample. This involves the alpha decay of Sm to Nd with a half-life of 1. Accuracy levels of within twenty million years in ages of two-and-a-half billion years are achievable. This involves electron capture or positron decay of potassium to argon Potassium has a half-life of 1. This is based on the beta decay of rubidium to strontium , with a half-life of 50 billion years.
This scheme is used to date old igneous and metamorphic rocks , and has also been used to date lunar samples. Closure temperatures are so high that they are not a concern. Rubidium-strontium dating is not as precise as the uranium-lead method, with errors of 30 to 50 million years for a 3-billion-year-old sample. A relatively short-range dating technique is based on the decay of uranium into thorium, a substance with a half-life of about 80, years. It is accompanied by a sister process, in which uranium decays into protactinium, which has a half-life of 32, years.
While uranium is water-soluble, thorium and protactinium are not, and so they are selectively precipitated into ocean-floor sediments , from which their ratios are measured. The scheme has a range of several hundred thousand years. A related method is ionium—thorium dating , which measures the ratio of ionium thorium to thorium in ocean sediment. Radiocarbon dating is also simply called Carbon dating. Carbon is a radioactive isotope of carbon, with a half-life of 5, years, [25] [26] which is very short compared with the above isotopes and decays into nitrogen.
Carbon, though, is continuously created through collisions of neutrons generated by cosmic rays with nitrogen in the upper atmosphere and thus remains at a near-constant level on Earth. The carbon ends up as a trace component in atmospheric carbon dioxide CO 2.