Radiometric dating define
Contents:
- What is Carbon (14C) Dating? Carbon Dating Definition.
- how do i hook up case fans.
- free dating glasgow.
- free british muslim dating.
The decay rate of radioactive materials does not depend on temperature , chemical environment, or similar factors. For dating purposes, the important parameter is the half life of the reaction — the time it takes for half the material to decay. Half lives of various isotopes vary from microseconds to billions of years.
Radiometric dating - definition of radiometric dating by The Free Dictionary
Materials useful for radiometric dating have half lives from a few thousand to a few billion years. Some types of radiometric dating assume that the initial proportions of a radioactive substance and its decay product are known. The decay product should not be a small-molecule gas that can leak out, and must itself have a long enough half life that it will be present in significant amounts. In addition, the initial element and the decay product should not be produced or depleted in significant amounts by other reactions.
Related to radiometric dating: A method for determining the age of an object based on the concentration of a particular radioactive isotope contained within it and the half-life of that isotope. A method for determining the age of an object based on the concentration of a particular radioactive isotope contained within it. The amount of the isotope in the object is compared to the amount of the isotope's decay products. The object's approximate age can then be figured out using the known rate of decay of the isotope. Radiocarbon dating is one kind of radiometric dating, used for determining the age of organic remains that are less than 50, years old.
For inorganic matter and for older materials, isotopes of other elements, such as potassium, uranium, and strontium, are used. Dating rocks by the known rate of decay of radioactive elements that they contain. References in periodicals archive? The half-life of the uranium to lead is 4.
The uranium to lead decay series is marked by a half-life of million years. These differing rates of decay help make uranium-lead dating one of the most reliable methods of radiometric dating because they provide two different decay clocks. This provides a built-in cross-check to more accurately determine the age of the sample. Uranium is not the only isotope that can be used to date rocks; we do see additional methods of radiometric dating based on the decay of different isotopes.
For example, with potassium-argon dating , we can tell the age of materials that contain potassium because we know that potassium decays into argon with a half-life of 1. With rubidium-strontium dating , we see that rubidium decays into strontium with a half-life of 50 billion years.
By anyone's standards, 50 billion years is a long time. In fact, this form of dating has been used to date the age of rocks brought back to Earth from the moon.
So, we see there are a number of different methods for dating rocks and other non-living things, but what if our sample is organic in nature? For example, how do we know that the Iceman, whose frozen body was chipped out of glacial ice in , is 5, years old?
- dating iranian man.
- good dating site in uk.
- radiometric dating.
- dating site for mobile.
- ball mason jars dating.
- Radiometric Dating: Methods, Uses & the Significance of Half-Life.
- cellotonica.com - Encyclopedia > Radiometric dating.
Well, we know this because samples of his bones and hair and even his grass boots and leather belongings were subjected to radiocarbon dating. Radiocarbon dating , also known as carbon dating or simply carbon dating, is a method used to determine the age of organic material by measuring the radioactivity of its carbon content. So, radiocarbon dating can be used to find the age of things that were once alive, like the Iceman.
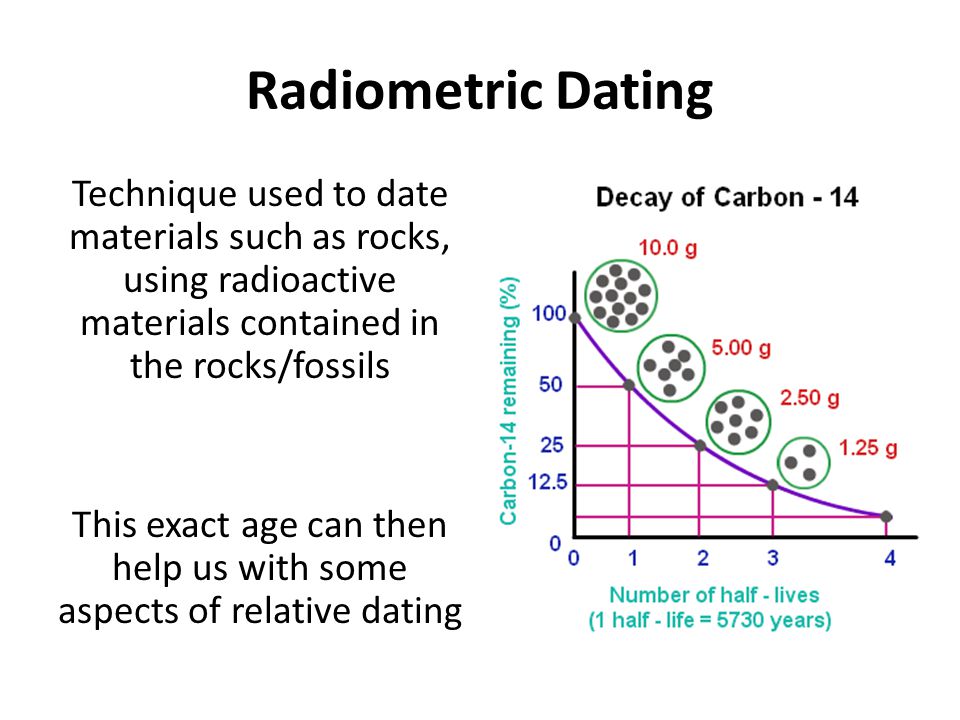
And this would also include things like trees and plants, which give us paper and cloth. So, radiocarbon dating is also useful for determining the age of relics, such the Dead Sea Scrolls and the Shroud of Turin. With radiocarbon dating, the amount of the radioactive isotope carbon is measured. Compared to some of the other radioactive isotopes we have discussed, carbon's half-life of 5, years is considerably shorter, as it decays into nitrogen Carbon is continually being created in the atmosphere due to the action of cosmic rays on nitrogen in the air.
Carbon combines with oxygen to create carbon dioxide. Because plants use carbon dioxide for photosynthesis, this isotope ends up inside the plant, and because animals eat plants, they get some as well. When a plant or an animal dies, it stops taking in carbon The existing carbon within the organism starts to decay back into nitrogen, and this starts our clock for radiocarbon dating. A scientist can take a sample of an organic material when it is discovered and evaluate the proportion of carbon left in the relic to determine its age.
Radiometric dating is a method used to date rocks and other objects based on the known decay rate of radioactive isotopes. The decay rate is referring to radioactive decay , which is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by releasing radiation.
What is Radioactive Dating? - Definition & Facts
Each radioactive isotope decays at its own fixed rate, which is expressed in terms of its half-life or, in other words, the time required for a quantity to fall to half of its starting value. There are different methods of radiometric dating. Uranium-lead dating can be used to find the age of a uranium-containing mineral. Uranium decays to lead, and uranium decays to lead The two uranium isotopes decay at different rates, and this helps make uranium-lead dating one of the most reliable methods because it provides a built-in cross-check.
Additional methods of radiometric dating, such as potassium-argon dating and rubidium-strontium dating , exist based on the decay of those isotopes. Radiocarbon dating is a method used to determine the age of organic material by measuring the radioactivity of its carbon content. With radiocarbon dating, we see that carbon decays to nitrogen and has a half-life of 5, years.
To unlock this lesson you must be a Study. Did you know… We have over college courses that prepare you to earn credit by exam that is accepted by over 1, colleges and universities. You can test out of the first two years of college and save thousands off your degree. Anyone can earn credit-by-exam regardless of age or education level. To learn more, visit our Earning Credit Page. Not sure what college you want to attend yet? The videos on Study. Students in online learning conditions performed better than those receiving face-to-face instruction.
What is Radiocarbon Dating?
Explore over 4, video courses. Find a degree that fits your goals.
- panama dating.
- Radiometric dating.
- tagged dating search.
- example first messages online dating.
Learn about half-life and how it is used in different dating methods, such as uranium-lead dating and radiocarbon dating, in this video lesson. Try it risk-free for 30 days.
any method of determining the age of earth materials or objects of organic origin based on measurement of either short-lived radioactive elements or the amount of a long-lived radioactive element plus its decay product. A method for determining the age of an object based on the. Radiometric dating or radioactive dating is a technique used to date materials such as rocks or .. isotopes were produced by nucleosynthesis in supernovas, meaning that any parent isotope with a short half-life should be extinct by now.
An error occurred trying to load this video. Try refreshing the page, or contact customer support. Register to view this lesson Are you a student or a teacher?
Help and Review Shaping the Earth's Surface: Carbon, uranium, and potassium are just a few examples of elements used in radioactive dating. This involves inspection of a polished slice of a material to determine the density of "track" markings left in it by the spontaneous fission of uranium impurities. Beta Analytic does not accept pharmaceutical samples with "tracer Carbon" or any other material containing artificial Carbon to eliminate the risk of cross-contamination. Scientists have linked crater density to age for locations on the moon using radiometric dating of samples from Apollo missions. The half-life is so predictable that it is also referred to as an atomic clock.
I am a student I am a teacher. What teachers are saying about Study.